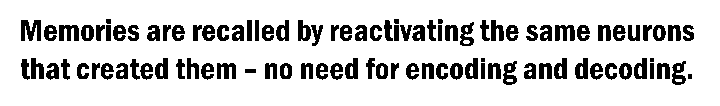The Concept Behind It
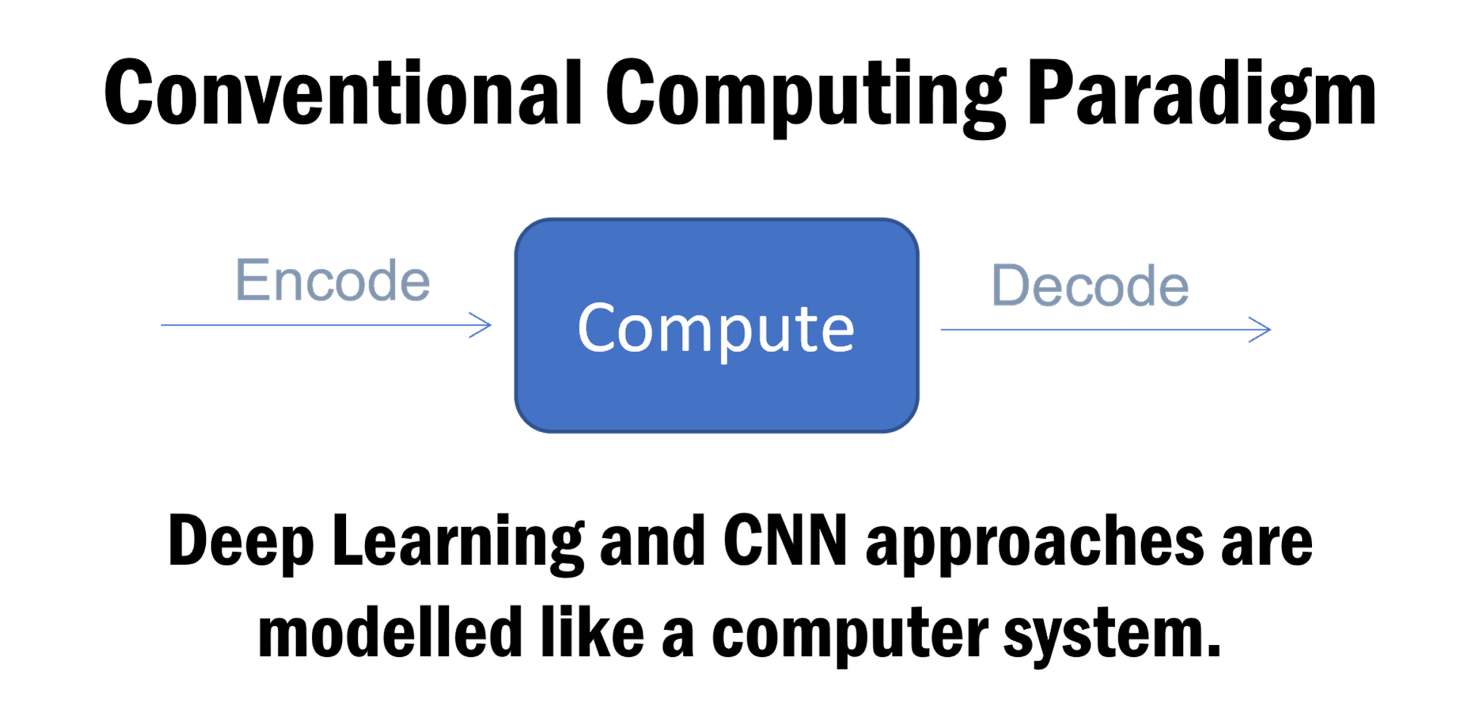
NeuraBase™ technology enables machines to learn tasks using defined elementary neurons, such as sensor or motor neurons, mimicking essential elements of biological intelligence. Built upon a novel approach to constructing adaptive neural networks, NeuraBase™ offers unique capabilities that allow for the creation of networks significantly larger and faster than conventional neural models.
The global momentum in neuroscience is driven by the belief that the human brain stores and recalls meaningful associations of events – memories. Understanding the structure and associations behind these events could pave the way for replicating them, ultimately enabling the development of truly intelligent systems and devices.
NeuraBase™ is founded on an alternative theory of brain function. To achieve true Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), a system must continuously learn from new inputs while retaining and recalling prior knowledge.
Intelligent interactions with our environment occur in sequences. Hearing, for example, is a sequence of sounds; speech is a sequence of articulatory muscle movements; and vision is processed through a sequence of saccadic eye movements. Thus, the ability to learn and recognise these sequences is fundamental.
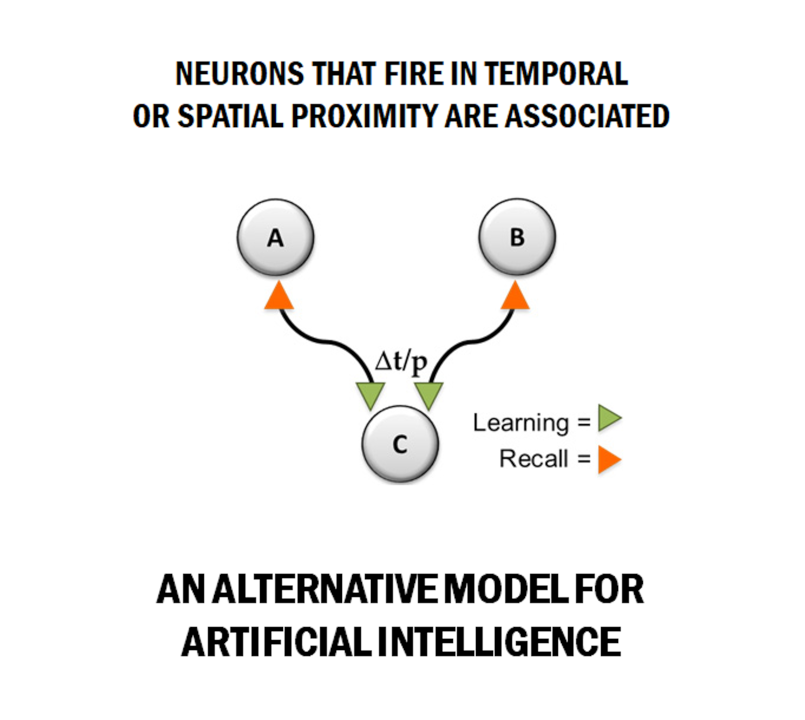
In NeuraBase™, sequences of events are encoded in a network of neurons, either spatially or temporally, organised hierarchically as a multi-level, multi-layer network. Each neuron represents a unique sequence of events and can be recalled by reactivating the same neurons involved in its creation, up to the elementary neuron level.
A single neuron can participate in thousands of associations with other neurons. The strength of each association is defined by synaptic weights. Depending on a set weight threshold, a neuron can express different associations. For instance, a neuron representing the phrase “Lucy is ” may be linked to neurons such as “playing ”, “sitting ” or “reading ”, allowing the system to generate sentences like “Lucy is playing ”, “Lucy is sitting ” or “Lucy is reading ”. Further associations, such as “on the ”, can compound this expression to form more complex sentences, even ones the system has never leant before. This demonstrates NeuraBase™’s inherent capacity for abstraction and creativity.
As more information is processed, NeuraBase™ becomes increasingly efficient. Fewer neurons are needed to store more data, as foundational building blocks already exist from earlier learning experiences. Frequently used neurons are reused, meaning the network depth does not need to be excessively large.
NeuraBase™ can be used to rapidly build neural networks ranging from 4 billion (using 32-bit pointers) to 280 trillion (using 48-bit pointers) neurons, with each neuron consisting of only four pointers, making it exceptionally memory-efficient. This allows for ultra-fast and highly accurate processing and mining of large-scale datasets.
Moreover, multiple NeuraBase™ models can be integrated into a multi-dimensional neural network, enabling multi-functionality. For example, a vision-based NeuraBase™ can be combined with a speech-based one, fusing visual and auditory capabilities into a single cohesive system. This presents exciting possibilities across various domains, including high-throughput language translation, bioinformatics, robotic control, speech, semantic analysis, reinforcement learning, and more.